2. Layers of the Earth
According to the chemical composition the Earth is divided into three layers: crust (=corteza), mantle (=manto) and core (=núcleo).


Apart from chemical composition we can divide the Earth according to the physical properties. We are going to study only the lithosphere, that consists of the upper part of the mantle and the crust. The lithosphere can slide over the rest part of the mantle

The mantle is composed of peridotite (a type of rock) but it has different physical properties in the upper and lower part. The crust and the upper part of the mantle have similar physical properties and this is why we consider it as a layer: the litosphere.
3. Plate tectonics
A plate is a piece of lithosphere that can move itself. As you can see, a plate
Plate tectonics (=Teoría de la Tectónica de Placas) is the theory that explains the structure and internal geologic processes of the Earth. This theory states that the lithosphere, the outer layer of the Earth, is divided into plates that move around the Earth.
A plate is a piece of lithosphere that can move and slide over the upper part of the mantle. As you can see in the picture, a plate can be composed of both continental and ocean lithosphere. Europe belongs to the Eurasian plate.

The distribution of continents and oceans is changing very slowly because of the movement of plates. 200 million year ago the continents where together forming a single continent called Pangea. Then the super continent Pangea began to split.

In the boundary of plates occur the creation and destruction of lithosphere, the formation of mountains, the earthquakes…
3.1 Convection currents and movement of plates
The cause ot the movement plates may be the convection currents in the mantle. Convection is the transfer of heat produced by the movement of molecules in liquids and gases. Convection also occurs in atmospheric currents (unit 9) and in boiling water: the warmer molecules rise up and cooler molecules descend, creating currents (=corrientes).

This happens in the mantle, and may explain the movement of plate tectonics. Nowadays is not completely clear what causes this movement and scientifics do not agree.

3.2 Plate boundaries
A plate boundary is a place where two tectonic plates meet. In the following figure the black lines are the plate boundaries. The red arrows indicates if the plates are separating or colliding.

There are three types of boundaries: convergent, divergent and transform depending on the movement of the plates:


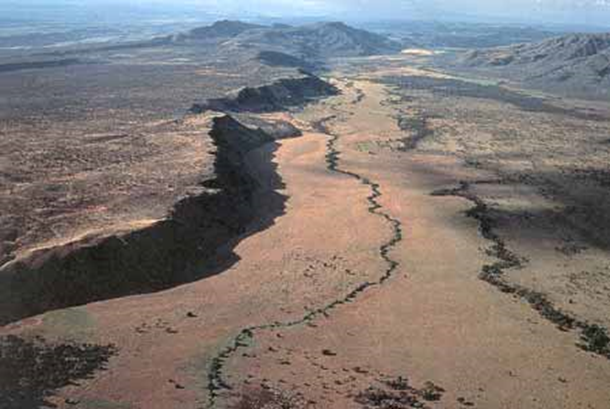
The East African Rift Valley is an example of a divergent boundary in an area of continental crust



4. Volcanism



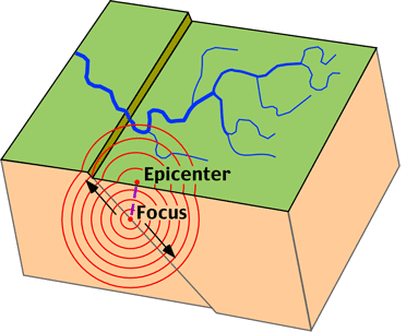
4. Earthquake